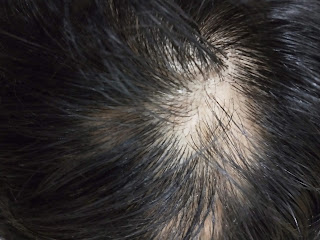
Alopecia areata is the sudden hair loss where coin like Bald patches are seen on the scalp.
It is an autoimmune condition in which the hair losses unpredictable.
It can occur in any age. Most cases are seen in the age before 30 years.
It can be seen in any gender.
In this condition, our n immune system attacks our own hair follicles. Due to which hair follicles shrink, and hairs fall down.
Links and associations+
1. The person suffering from allopathic areata has a greater risk of having other autoimmune diseases like thyroiditis, vitiligo, pernicious anaemia
2. Collagen vascular diseases
3. Common with down syndrome
4. Stress, anxiety, depression
Extreme stress is a trigger for allopathy areata.
Symptoms-
1. Hair loss- round, coin sized bald patches on scalp
2. Hair loss can be sudden or develop in some days or weeks.
3. The area of hair loss appears smooth
4. Sometime,s growth of beard and eyelashes are also affected
5. No Itching, redness or burning sensation over the scalp
6. Nails - small dents, white spots or lines
Types-
1. Localised allopesha areata - hair fall occurs in small, localised patches
2. Alopecia areata totalis- complete hair loss over the scalp
3. Alopecia areata universalis- hair loss occurs a over the full body, that is from scalp eyebrows eyelashes beard and gradually from all over the body.
4. Diffuse alopecia areata- appears like male or female pattern baldness.
5. Ofiatic alopecia area- hair loss occurs on the sides are back of scalp
Diagnosis-
1. Biopsy
2. Blood tests
The chances of recovery are high
Allopesha areata is a recurrent condition. That is it can occur again and again at an interval of few months or years.
Myths+
1. Caused by a worm
2. Side effect of a drugg or medicine
3. Related to any food or water
4. Can be treated by applying coconut oil or onion juice